Currently, talk of STIs is not the taboo that it used to be. It isn’t perhaps our topic of choice with friends and family, but there is much more advice, help and education on sexually transmitted infections than ever before.
Chlamydia is the most common STI, with around 200,000 people across the UK diagnosed with the infection each year, https://www.thesun.co.uk/fabulous/3967879/sexual-health-sexually-transmitted-infections-symptoms-sti/ and syphilis becoming the fastest-growing sexual infection, but there is one STI you may not have heard of.
Trichomoniasis
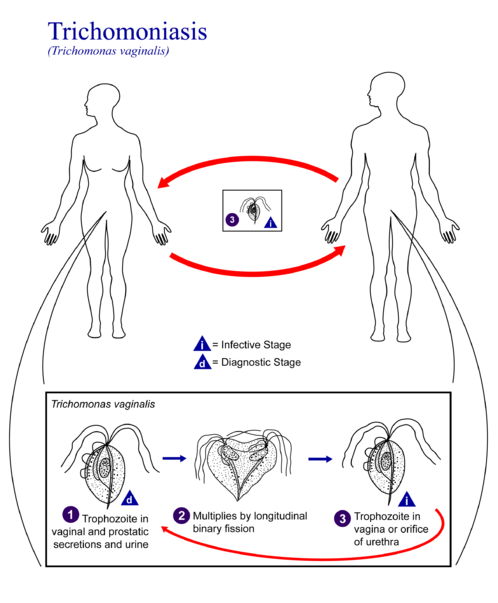
Trichomoniasis is caused by a tiny parasite known as Trichomonas Vaginalis (TV). It is normally spread by sharing unwashed sexual devices and toys or having unprotected sex.
In women, the parasite primarily infects the urethra and vagina, whereas in men, TV infects the urethra but is also known to infect the prostate gland or head of the penis.
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
Perhaps the most frightening aspect of Trichomoniasis is that around half of women and men show no symptoms whatsoever, with some sufferers falsely thinking they have contracted a different disease or illness.
For home STI kits in London to conduct your own test for common STIs, contact a clinic such as https://www.bexleysexualhealth.org/chlamydia_screening/.
The symptoms are similar to those of other sexual transmitted infections, such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia.
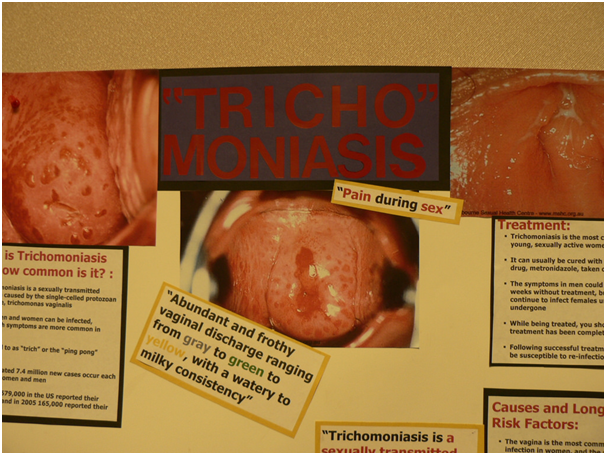
If you are a woman, the key symptoms are vaginal discharge that can be unpleasant smelling, thin, frothy, or thick with a yellow-green colour along with swelling, itching and soreness around the vagina. It can also be painful to have sex or urinate if you are suffering from trichomoniasis.
Even the inner thighs are known to become itchy as a symptom of trichomoniasis.
In men, symptoms include pain during ejaculation or urination and the need to urinate more frequently. There can also be white discharge emitted from the penis as well as redness, soreness and swelling around the foreskin or head of the penis.
What to do if you may have Trichomoniasis
If you might have Trichomoniasis or any other sexually transmitted infection, it is important to visit your nearest sexual health clinic or GP as soon as possible.
A swab test will be conducted, which will diagnose whether you do have the infection. It can be treated with antibiotics.



